[데이터 통신] 5. 아날로그 전송(Analog Transmission)
2023.02.13- -
일반적으로 Digital Transmission이 바람직하나, digital transmission을 위해서는 DC 성분을 주변으로한 low pass channel이 필요하게 된다.
그런데 만약에 신호를 전달해야 하는데 channel 자체가 특정 주파수 대역(bandwidth)를 가질 때 digital transmission을 어쩔 수 없이 사용하지 못하고 특정 주파수 대역으로 modulation(변조)한 analog transmission을 해야한다.
5.1 Digital-to-Analog Conversion
Digital-to-Analog Conversion(D/A Conversion)
- Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data
- digital data information에 근거해서 analog signal의 특성 중 하나를 바꾸는 과정을 D/A Conversion이라고 한다.

Types of Digital-to-Analog Modulation

QAM방식이 효율성 측면에서 좋아 가장 많이 사용됨.
Aspects of D/A Conversion
- Data element versus signal element
- 2개의 data element(2 bit)를 1개의 signal element에 보내는 것이 일반적
- Data rate (bit rate) versus signal rate (baud rate)
- S = N x 1/r baud
- S (signal rate), N (data rate),
- r (number of data element in one signal element)
- Bit rate: bits per second (in bps)
- Baud rate: signal elements per second (in baud)
- Bit rate <= baud rate
- '='인 경우는 r=1인 경우
- S = N x 1/r baud
- Carrier signal (carrier frequency)
- High-frequency signal used to modulate the information
- Modulated signal: information modulated by the carrier signal
- digital data를 analog data로 modulation 할 때, DC 주변의 baseband에 있는 신호에 해당하는 것들을 bandpass 형태로(특정 주파수 대역으로) 보내기 위해서는 그 주파수 대역에 맞는 high frequency signal이 필요하게 된다. 그래서 우리가 보내고 싶어하는 data를 modulation 하기 위해서 사용되는 frequency signal을 말한다.
Examples 5.2
- An analog signal has a bit rate of 8000bps and a baud rate of 1000 baud. How many data elements are carried by each signal element? How many signal elements do we need?
Solution
S = 1000, N = 8000, and r and L are unknown. We find first the value of r and then the value of L.

r = 8, 즉 한 signal이 보내는 bit수가 8이라는 것이므로 data element는 28 = 256 개이다.
ASK : Binary ASK
ASK(Amplitude Shift Keying)
- the amplitude of the carrier signal is varied to create signal elements. Both frequency and phase remain constant.
- BASK or OOK (on-off keying)
- Bandwidth for ASK: B=(1+d) x S
- 1: original carrier signal
- 0: zero signal
- d: 목적지에 도착하면 filter를 통해 뽑아낼텐데 이 때 loss 등을 고려했을 때 d 만큼의 오차가 생길 것이다.(0~1 사이의 값; 1 is worst case)
- 이론적으로는 signal rate에 준하는 bandwidth를 요구하지만 실질적으로는 modulation에서의 오버헤드나 filter가 정확히 cut을 하지 못한다는 문제가 있기 때문에 d 만큼의 양을 더 추가한 것이다.
- 그래서 'signal rate의 최대 2배까지도 필요할 수도 있다' 라는 것을 의미한다.

fc(carrier frequency) 주변의 주파수에 맞춰서 보낸다.
Implementation of Binary ASK

고주파의 carrier signal을 oscillator로 만들어 내고 original digital signal과 곱하면 된다.
Example: Full-duplex ASK
- In data communications, we normally use full-duplex links with communication in both directions.
- We need to divide the bandwidth into two with two carrier frequencies.
- In this example, the available bandwidth for each direction is now 50 kHz, which leaves us with a data rate of 25 kbps in each direction.
- d=1인 경우 (최악의 경우) signal rate은 bandwidth의 절반인 25kbps이다.
- 보낼 때는 225kHz로 받을 때는 275kHz로 전달을 한다.

FSK : Bianary FSK
FSK(Frequency Shift Keying)
- the frequency of the carrier signal is varied to represent data. Both peak amplitude and phase remain constant.
- Bandwidth for FSK: B = (1 + d) x S + 2Δf

- 데이터 값에 따라서 주파수를 달리하는 방식.
- 주파수가 높으면 1, 낮으면 0
- 추가적으로 두 carrier 주파수의 차이의 두 배가 더 더해진 bandwidth가 요구된다.
- ASK보다 더 높은 bandwidth를 요구한다.
BFSK: Example
- We have an available bandwidth of 100 kHz which spans from 200 to 300 kHz. What should be the carrier frequency and the bit rate if we modulated our data by using FSK with d = 1?
The midpoint of the band is at 250 kHz. We choose 2Δf to be 50 kHz; this means


Implementation of Binary FSK

VCO: 입력되는 volatge level(digital)에 따라서 출력 주파수 신호에 주파수 성분을 달라지게 만드는 역할이다.
Multilevel FSK(중요)
- carrier frequency가 여러개
- The frequencies need to be 2Δf apart. Min. value 2Δf needs to be S.
- B = (1 + d) x S + (L – 1) 2Δf → B = L x S with d = 0
- Example: We need to send data 3 bits at a time at a bit rate of 3 Mbps. The carrier frequency is 10 MHz. Calculate the number of levels (different frequencies), the baud rate, and the bandwidth
- L = 23 = 8. The baud rate is S = 3 Mbps/3 = 1 Mbaud.
- This means that the carrier frequencies must be 1 MHz apart (2Δf = 1 MHz). The bandwidth is B = 8 × 1 = 8 MHz.

PSK: Binary PSK
PSK(Phase Shift Keying)
- the phase of the carrier is varied to represent two or more different signal elements. Both peak amplitude and frequency remain constant.
- Bandwidth: the same as BASK, B = (1+d) x S
- Less than that for BFSK
- No bandwidth waste for separating two carrier signals.
- 1일 때는 정상, 0일 때는 phase shift by 180 degrees
- phase를 달리해도 carrier frequency(주파수 자체)는 같기 때문에 주파수 도메인에서 1개의 carrier frequency를 갖는다.

PSK vs. ASK
PSK와 ASK 는 FSK에 비해서 Bandwidth를 적게 요구한다는 장점이 있는데 이 둘간의 차이점은 무엇일까?
- ASK: amplitude가 신호 레벨을 결정
- PSK: Phase가 어떻게 되어있는지에 따라 신호 레벨을 결정
신호 전달할 때는 여러가지 impairment가 존재했는데(CH4), 이 중 특히 noise가 original signal의 amplitude는 쉽게 변하게 할 수 있지만 phase는 쉽게 변하게 하지 못한다.
따라서 amplitude에 기반한 ASK는 noise에 쉽게 영향을 받지만 PSK는 noise에 크게 영향을 받지 않기 때문에 PSK가 noise 관점 측면에서 더 좋은 성능을 보인다(복구를 쉽게 할 수 있음).
Implementation of binary PSK

1이면 5V 0이면 -5V를 입력
반전 입력을 통해 PSK를 구현한다.
Quadrature PSK

앞자리와 뒷자리를 기준으로 bit를 split하여 각 signal에 대해 phase shift를 결정하고 이후에 이 두 signal에 대한 summation을 진행한다.
이를 통해 4종류의 phase 형태가 나오게 된다.(초록색 부분)
Constellation Diagram
- Define the amplitude and phase of a signal element
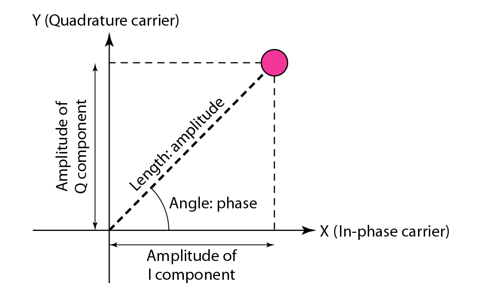
Constellation Diagram: Examples

QAM
- Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Combination of ASK and PSK
- Amplitude와 Phase 모두에 변화를 줌
- Bandwidth: the same as that required for ASK and PSK

- 골고루 분산시키는 것이 효율적이다.
- 많은 신호를 만들어낼 수 있다는 것은 하나의 signal이 여러개의 data를 나를 수 있게 된다는 의미이기 때문에 굉장히 효율적인 것이다.
5.2 Analog-to-Analog Modulation
일반적으로 가지고 있는 analog 신호는 DC(low pass)부터 시작하여 낮은 주파수 대역에 분포되어 있는 신호 형태이다. 하지만 우리가 보내야 하는 전송 channel이 특정 주파수 대역의 band pass 특성을 갖고 있다면 이 low pass 특성을 갖고 있는 신호를 modulation 시켜서 carrier frequency를 가지고 특정 주파수 대역으로 옮겨서 해당 주파수 대역을 통해서 전달할 수밖에 없다.
- Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal
- Modulation is needed if the medium is bandpass in nature or if only a bandpass channel is available to us

Amplitude Modulation(AM)
- the carrier signal is modulated so that its amplitude varies with the changing amplitudes of the modulating signal.
- The total bandwidth required for AM can be determined from the bandwidth of the audio signal:
- BAM = 2B.
- Modulating signal: 변조 시킬 대상(signal)

AM Band Allocation
- Bandwidth of an audio signal (speech and music) is usually 5 kHz

AM 방송이 band를 allocation 할 때에는 기본적으로 2배의 bandwidth를 갖게 간격을 유지하되 signal간의 interference 까지 생각하여 두 배 이상의 거리를 떨어뜨려 AM bandwidth를 가지고 AM 방송이 된다.
Frequency Modulation(FM)
- The total bandwidth required for FM can be determined from the bandwidth of the audio signal:
- BFM = 2(1 + β)B.
- β: modulating technique에 따라 달라지며 보통 '4'의 값을 가짐.

AM 보다 훨씬 더 넓은 대역폭을 요구한다.
FM Band Allocation
FM 방송은 음악방송이 많기 때문에 스테레오나 하이파이와 같은 것 때문에 방송이 되는 신호의 자체 bandwidth가 훨씬 더 넓은 15kHz 정도이다.
- Bandwidth of an audio signal (speech and music) broadcast in stereo is almost 15 kHz
- FCC allows 200 kHz for each station (β =4 with some extra guard band) ; 10배 이상
- FM 방송사와 방송사 간에 최소 200kHz를 띄워 놓도록 하였다.
- 원래는 15kHz의 10배(β =4)인 150kHz의 주파수 대역을 갖지만 옆 채널로부터 방해가 되는 interference(간섭) 등을 고려하여 200kHz를 extra guard band로 지정하였음.(FCC에서)
- Separated by at least 200 kHz

Phase Modulation
FM과 매우 유사
- The total bandwidth required for PM can be determined from the bandwidth and maximum amplitude of the modulating signal: BPM = 2(1 + β)B.

- FM은 신호를 신호의 amplitude의 크기에 따라서 VCO 즉, Oscillator의 주파수를 직접 변조하는 것이라면,
- PM은 신호의 변화율(미분값)에 따라 Frequency Oscillator의 주파수를 변조시키는 것이다.
'CS 지식 > 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터 통신] 7. 전송 매체(Transmission Media) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
|---|---|
| [데이터 통신] 6. Bandwidth Utilization Multiplexing & Specturm Spreading (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 4. 디지털 전송(Digital Transmission) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 3. 물리계층 이해(Introduction to Pysical Layer) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 2. 네트워크 모델(Network Models) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
소중한 공감 감사합니다