[운영체제 | OS] 1. 운영체제 시작
2023.01.23- -
운영체제란?
- 사용자의 컴퓨터와 컴퓨터 하드웨어 사이에서 중개 역할을 하는 프로그램
- 운영체제의 목표:
- 사용자 프로그램을 실행하고 사용자 문제 해결을 더 쉽게 만든다.
- 사용자가 프로그램을 실행할 수 있는 환경을 제공한다.
- 컴퓨터 시스템을 더 편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 한다.(편리성; convenience)
- 컴퓨터 하드웨어를 더 효율적으로 사용한다.(효율성; efficiency)
컴퓨터 시스템 구조
컴퓨터 시스템은 네 가지 구성 요소로 나눌 수 있다:
- 하드웨어(Hardware) - 기본적인 컴퓨팅 자원을 제공한다.
- CPU, 메모리, I/O장치
- 운영체제(Operating system)
- 여러 애플리케이션과 사용자 사이에서 하드웨어 사용을 제어하고 조정한다.
- 애플리케이션 프로그램(Application Programs) - 시스템 자원을 사용하여 사용자 컴퓨팅 문제를 해결하는 방법을 정의한다.
- 워드 프로세서, 컴파일러, 웹 브라우저, 데이터베이스 시스템, 비디오 게임
- 사용자(Users)
- 사람, 기계, 다른 컴퓨터 - 컴퓨터를 사용하는 주체
컴퓨터 시스템의 4가지 구성요소

운영체제가 하는 일
운영체제가 하는 일은 관점에 따라 다르다고 할 수 있다.
사용자는 편리성, 사용 용이성 및 성능을 원하지만 자원 활용도에는 신경 쓰지 않는다.
하지만 메인프레임이나 미니컴퓨터와 같은 공유 컴퓨터는 모든 사용자를 만족시켜야 한다. 즉, 한 사용자만 만족시키는 것이 아니라 다른 많은 사람들에게도 만족할만 한 서비스를 제공해야 한다.
- 워크스테이션과 같은 전용 시스템의 사용자는 전용 자원을 가지지만 서버에서는 일반적으로 공유 자원을 자주 사용한다.
- 휴대용 컴퓨터는 자원이 부족하고 사용성 및 배터리 수명을 최적화해왔다.
- 일부 컴퓨터는 디바이스와 자동차에 내장된 컴퓨터처럼 사용자 인터페이스(UI)가 거의 없거나 아예 없다.
운영체제의 정의
- OS는 자원 할당자이다.
- 모든 자원을 관리하는 주체로서 역할을 한다.
- 효율적이고 공정한 자원 사용을 위해 충돌하는 요청들 사이에서 결정을 내린다.
- OS는 제어 프로그램이다.
- 프로그램 실행을 제어하여 오류와 부적절한 컴퓨터 사용을 방지한다.
- "컴퓨터에서 항상 실행 중인 하나의 프로그램"이 있는데 이는 커널이라고 한다.
그외의 것들은 시스템 프로그램(운영 체제외 함께 제공됨), 또는 애플리케이션 프로그램이라고 분류할 수 있다.
컴퓨터 시스템 조직 - Computer System Organization
- Computer-system operation
- 컴퓨터 시스템의 동작
- 하나 이상의 CPU를 탑재한 디바이스 컨트롤러는 공유된 메모리에 대한 접근을 제공하는 common bus를 통해 연결된다.
- 메모리 사이클 동안 경쟁하는 CPU와 디바이스의 동시적인 실행이 이루어진다. (메모리 컨트롤러)
- mesh, switch 방식으로 하면 효율은 좋겠지만 cost가 비싸다 -> 그래서 common bus를 이용하는 것이다.
- CPU와 controller가 동시에 돌아간다.
- bus master가 두 개 이상이면 충돌이 일어난다.
(근데 CPU 뿐만 아니라 disk controller도 master가 될 수 있기 때문에 bus arbitray가 있어야 함.)

컴퓨터 시스템 동작 - Computer-System Operation
- I/O 디바이스와 CPU는 동시에 실행될 수 있다.
- 각 디바이스 컨트롤러는 저마다 디바이스 특정 유형을 담당한다.
- 각 디바이스 컨트롤러는 local buffer를 갖는다.
- CPU는 메인 메모리와 local buffer 간에 데이터를 주고받는다.
- I/O는 디바이스에서 컨트롤러의 local buffer로 이동하는 흐름을 갖는다.
- 디바이스 컨트롤러는 CPU에게 interrupt가 발생하여 동작이 종료되었음을 알린다.
컴퓨터 부팅 - Computer Startup
bootstrap program은 전원을 켜거나 리붓 할 때 로드된다.
- bootstrap program: OS를 탑재시키는 프로그램(ROM에 저장되는 firmware)
- 일반적으로 통상 firmware라고 알려진 ROM 혹은 EPROM에 저장된다.
- 시스템의 모든 부분을 초기화시킨다.
- 운영 체제 커널을 로드하고 실행을 시작한다.
OS는 한 번 시작된 이후에 이벤트를 기다리는 상태에 돌입한다.
- 그래서 OS는 능동적인 애가 아니라 외부에서 어떠한 서비스 요청이 들어왔을 때 반응하는 방식이기 때문에 그저 기다리고만 있는다.
- 즉, Event driven system
- 이벤트의 발생은 (HW든 SW든)interrupt에 의한 시그널이다.
- power failed -> hardware interrupt
Common Functions of Interrupts
- 외부에서 요청을 하지 않으면 OS는 일을 하지 않는다.
- Interrupt는 interrupt service routine(ISR)으로 제어를 전달하는데 이 때 interrupt vector가 사용되며, interrupt vector란 모든 interrupt service routines(ISR)의 주소를 포함하고 있는 벡터값이다.
- Interrupt 아키텍처는 방해된 명령의 주소를 반드시 저장해야 한다.
- ISR 실행 후 리턴을 하기 위함이다.
- interrupt 됐을 당시 address를 save를 해 놔야 처리 후 다시 돌아갈 수 있는 것이다.

- trap 혹은 exception은 소프트웨어로부터 발생된 interrupt의 일종으로 보통 에러나 유저 요청에 의해 발생되는 것들이라고 할 수 있다.
- OS는 interrupt driven 방식이다.
- system call(시스템콜)이란 OS가 가지고 있는 API를 의미한다.
- kernel 모드에서 주로 사용된다.
- library 함수(printf와 같은)는 User mode 에서만 사용되는 것들이다.
trap과 exception의 차이는 다음과 같다.
- trap: OS 함수를 호출하기 위해서 발생되는 (software) interrupt
- trap마다 번호가 있어 각 trap마다 해당하는 trap handler를 실행한 후 리턴한다.
- exception: divide by zero 등과 같이 프로그램에서 각종 error가 발생할 때의 software interrupt
Interrupt Handling
- OS는 register와 program counter를 저장하여 CPU의 상태를 보존한다.
- ISR 실행 후 리턴 시 원래의 snapshot을 복구시킴
- running snapshot
- 어떤 타입의 interrupt가 발생했는지 결정하기 위한 방식에는 다음과 같은 것들이 있다.
- polling
- CPU에 interrupt가 발생했다는 사실만 알려지고 interrupt를 누가 걸었는지는 모름
- 초창기에 사용되던 방식
- vectored interrupt system
- 어느 한 device가 interrupt를 걸면 CPU가 OK라는 응답을 보내고, 다시 그 device에서는 ok 사인에 대한 interrupt vector를 memory에 write하는 방식처럼 data bus에 실어 보낸다.
- polling
- 분리된 코드 세그먼트는 어떤 액션이 각 유형의 interrupt에 대해 수행되어야 하는지를 결정한다.
Interrupt Timeline

I/O device가 IO를 하고 있는 동안에도 CPU 역시도 일을 하고 있다.(concurrent)
위 그림을 보면 transfer done 단계에서 interrupt가 있었을 것이고 CPU에서는 그에 대해 ISR이 실행되는 구간이 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
스토리지 구조 - Storage Structure
- main memory(메인 메모리) - CPU가 직접적으로 접근할 수 있는 오로지 큰 스토리지 미디어
- Random access
- 일반적으로 volatile(휘발성) 성질임 -> power가 꺼지면 content가 날라가는 방식
- 2차 스토리지(HDD, SDD)
- 큰 nonvolatile(비휘발성) 저장 용량을 제공하는 메인 메모리의 확장버전이라고 볼 수 있다.
- 하드 디스크(Hard Disk) - 자기(magnetic) 기록 재료로 덮인 단단한 금속 또는 유리 플래터(platters)
- 디스크 표면은 논리적으로 트랙으로 나뉘며, 섹터로 세분화된다.
- 디스크 컨트롤러는 디바이스와 컴퓨터 사이의 논리적 상호작용을 결정한다.
- Solid-state disks(SSD) - 하드 디스크보다 더 빠름, 비휘발성
- 다양한 기술의 집약체
- 더 인기가 많아지는 중
스토리지 계층 - Storage Hierarchy
- 스토리지 시스템은 계층 구조를 갖는다.
- Speed
- Cost
- Volatility
- Caching – 정보를 더 빠른 스토리지 시스템으로 복사하는 것;
- 메인 메모리는 2차 스토리지를 위한 캐시로 보여질 수도 있다.
- Device Driver - 각 디바이스 큰트롤러가 I/O를 관리하기 위해 존재
- 컨트롤러와 커널 사이에 획일된 인터페이스를 제공한다.
스토리지 디바이스 계층 - Storage-Device Hierarchy
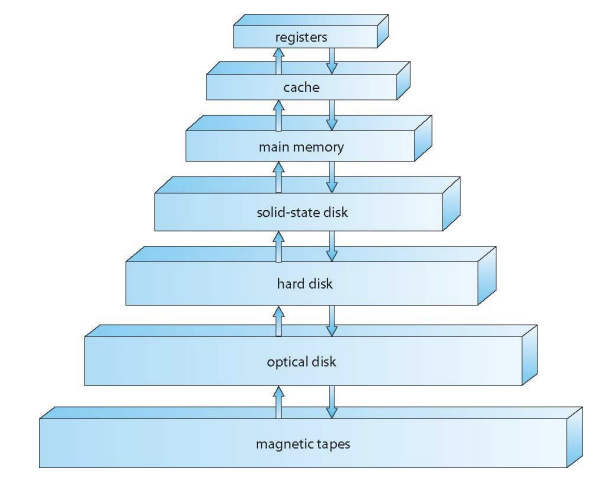
program을 실행시키기 위해서는 무조건 main memory에 탑재를 시켜야 한다.
cache는 각 계층 사이마다 있을 수 있다.
- 또한 여러 개의 캐시가 이어져서 사용되기도 함(L1 캐시, L2캐시)
캐싱 - Caching
- 컴퓨터 상의 굉장히 많은 단계에서 수행되는 중요한 principle이다.(in hardware, operating system, software..)
- 사용 중인 정보가 더 느린 스토리지에서 더 빠른 스토리지로 일시적으로 복사된다.
- 더 빠른 스토리지(cache)는 우선적으로 정보가 존재하는지를 먼저 체크한다.
- 만약 존재한다면, 정보를 바로 cache에서 가져온다.(fast)
- 만약 존재하지 않는다면, 데이터를 cache로 복사하고 그곳에서 가져온다.
- 캐시는 캐시되는 스토리지보다 더 작다.
- 캐시 관리는 중요한 디자인 문제 중 하나이다.
- 캐시 사이즈와 replacement policy(교체 정책-무엇을 버릴지 결정하는)도 중요하다.
I/O 구조 - I/O Structure
- 컴퓨터 시스템은 하나 이상의 CPU와 common bus를 통해 연결된 여러 개의 디바이스 컨트롤러들로 구성된다.
- 디바이스 컨트롤러는 local buffer storage와 특수 목적 register의 다발을 포함한다.
- 디바이스 컨트롤러는 본인을 제어하는 주변 장치와 local buffer storage의 사이에서 데이터를 전달하는 역할을 한다.
- OS는 각 디바이스 컨트롤러마다 디바이스 드라이버(device driver)를 갖는다.
- 각 device driver(disk, keyboard...) 마다 대화가 가능한 device controller가 있고 끼리끼리만 대화가 가능하다.
- device drivce는 디바이스 컨트롤러의 행동을 이해하고 OS에게 디바이스에 대한 획일된 인터페이스를 제공한다.
- Interrupt driven I/O 동작을 시작하기 위해선 아래 과정을 따른다.
- device driver가 device controller내의 register들을 로드한다.(command)
- device controller는 registers의 내용을 조사하여 그 명령을 인식한다.
- device controller는 디바이스와 local buffer간의 데이터를 전송시킨다.
- 한번 데이터가 전송을 완료하면, device controller는 그 사실을 interrupt를 사용하여 device driver에게 알린다. (data transfer 종료)
- Device driver는 OS로 제어가 되돌아가며, 데이터 혹은 그 데이터를 가르키는 포인터 및 상태 정보를 되돌린다.
Direct Memory Access(DMA) Structure
DMA는 CPU의 간섭없이 device to/from memory read/write하는 방법이다.
- 메모리 속도에 가까운 속도로 정보를 전송할 수 있는 high-speed I/O 디바이스에 사용된다.
- 디바이스 컨트롤러는 블럭 단위의 데이터를 buffer storage에서 곧바로 메인 메모리에게 CPU 간섭 없이 전달한다.
- 오직 하나의 interrupt만이 블럭 당 생성된다. (byte 당 하나의 interrupt가 생성되는 것이 아님)
현대의 컴퓨터가 동작하는 방식
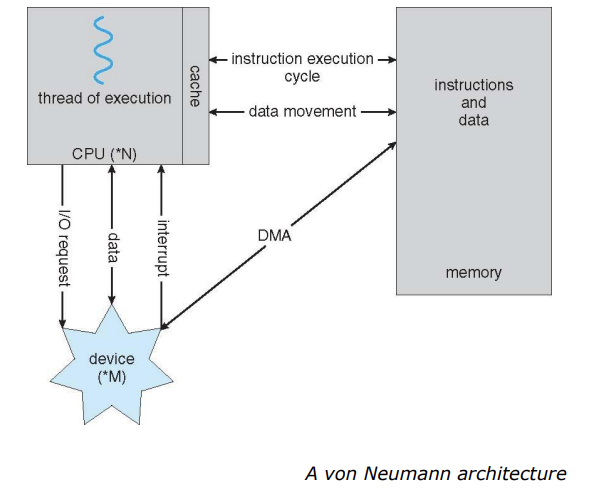
- 대부분의 컴퓨터는 위 사진과 같은 구조(폰노이만 아키텍처)를 갖는다.
- 폰노이만 구조를 해치지 않으면서 좀 더 효율적으로 read/write을 할 수 있는 방식이 없을까 해서 나온 것이 DMA
- DMA
- 원래는 CPU가 device controller로부터 값을 읽어서 memory에 전달해야 하는데 DMA는 device가 CPU는 쉬고 있을 때 어떤 data를 메모리에 가져다 놓겠다고 선언만 하고 나서 CPU 몰래 가져다 놓는 방식
- 가장 먼저 메모리에 탑재를 시켜야 함
- CPU가 한 번에 하나씩 명령(instruction)을 받아들여서
- 이 때, thread of execution이 여러 개가 될 수 있음 -> parallel processing
- I/O device + I/O controller
- CPU는 직접 I/O하지 않음(HDD와 같이 엄청 느린 디바이스를 상대할 시간이 없음) -> device controller가 대신 control
- 그 때부터 CPU와 device controller는 parallel하게(각자) 돌아간다.
폰노이만 아키텍쳐 - Von Neumann Architecture
- Stored Program 컨셉
- 프로그램과 데이터를 저장하는 메인 메모리
- 메모리의 내용이 주소에 의해 접근가능하다.
- 실행이 순차적으로 발생한다.(명시적으로 지정하지 않으면)
- PC(Program Counter) - CPU가 갖고 있는 register
- 다음에 실행할 instruction의 주소를 가지고 있음
어떤 프로그램도 아래 세 가지 operation에서 벗어나지 않는다.
- sequence
- iteration
- selection
The Von Neumann Architecture

내부에서 고정적으로 사용되는 memory -> CPU regiseter
Instruction Cycle
- Two steps:
- Fetch
- Execute

- instruction cycle = 한 명령 문장을 실행하는 한 cycle
- 왜 main memory에 탑재해야 하는가?
- CPU internal 메모리는 비싸기 때문에 많은 메모리를 탑재하지 못하고
- HDD는 속도가 너무 느리기 때문이다.

컴퓨터 시스템 아키텍쳐 - Computer-System Architecture
- Single-processor systems
- 대부분의 시스템은 단일 범용 프로세서를 사용한다.
- 대부분의 시스템은 특수 목적 프로세서도 갖는다.(디바이스 특화)
- 사용 및 중요성이 증가하는 멀티프로세서 시스템(multuprocessor system)
- parallel system(multi-core)로도 알려진, 강하게 결합된 시스템
- 강하게 결합된 시스템 - 프로세스는 메모리와 클럭을 공유한다.
- 통신은 일반적으로 가까운 지역에서 공유 메모리를 통해 이루어진다.(제한된 영역 내에서 공유되는)
- 장점은 다음과 같다.
- 증가한 throughput(처리량) (speed up)
- 규모의 경제성(Economy of scale) - 여러 단일 프로세스 시스템 보다 비용 절감
- 신뢰성(reliability) 향상 - 뛰어난 성능 저하 또는 내결함성(중복)
- Two types:
- Asymmetric Multiprocessing
- Symmetric Multiprocessing
- Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP)
- 각 프로세서는 동일한 운영 체제 복사본을 실행한다.
- 로드 밸런싱은 중요하다.
- 예를 들어 채점을 두 명이서 나눠서 하는데 한 사람은 만 명에 대해서, 한 사람은 10명에 대한 채점을 한다면 밸런스가 맞지 않아 비효율이 발생하는데 로드 밸런서가 이를 해결할 수 있다..
- 대부분의 현대 운영체제에서는 SMP를 지원한다.
- Asymmetric multiprocessing
- 각 프로레스에는 특정 작업이 할당된다. 마스터 프로세서는 슬레이브 프로세서에 작업을 예약하고 할당한다.
- 매우 큰 시스템에서 가장 흔히 볼 수 있다.
Symmetric Multiprocessing Architecture
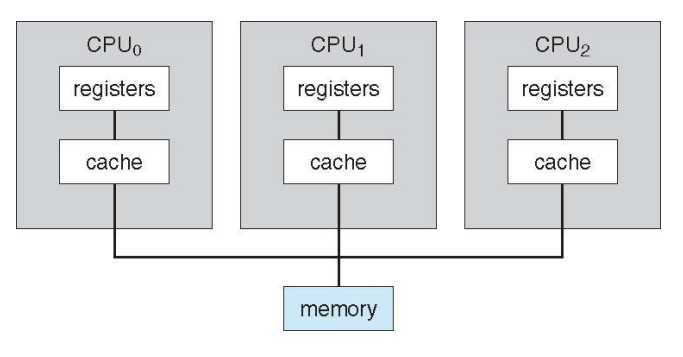
master-slave 관계가 아닌 동등한 관계
dependent 관계의 CPU들이 같이 일을 함.(memory를 공유하기 때문에)
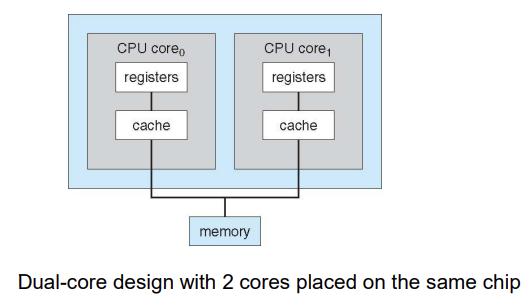
A Dual-Core Design
- Memory access model: UMA(uniform memory access ) and NUMA architecture variations
- Multiprocessing increases computing power by adding CPUs
- Adding CPUs also increases amount of memory addressable
- NUMA(non-uniform): 각 CPU가 memory에서 자주쓰는 내용을 가져와서 사용함.
- Multi-chip and multicore
- Blade server systems
- Chassis containing multiple independent multiprocessor systems
Clustered Systems
- 좀 더 독립성이 부여된 시스템들끼리 모여 있는 경우
- Another type of multiprocessor system
- multiple independent nodes working together
- Each node may be a single-processor system or multi-core system
- Loosely-coupled system, closely linked via LAN (Ethernet) or InfiniBand
- Usually sharing storage via a storage-area network (SAN)
- Provides a high-availability(HA) service which survives failures
- Asymmetric clustering has one machine in hot-standby mode
- Symmetric clustering has multiple nodes running applications, monitoring each other
- Some clusters are for high-performance computing (HPC)
- Applications must be written to use parallelization
- Other forms of Clusters
- Parallel cluster or clustering over WAN
- Some have distributed lock manager (DLM) to avoid conflicting operations
Clustered Systems
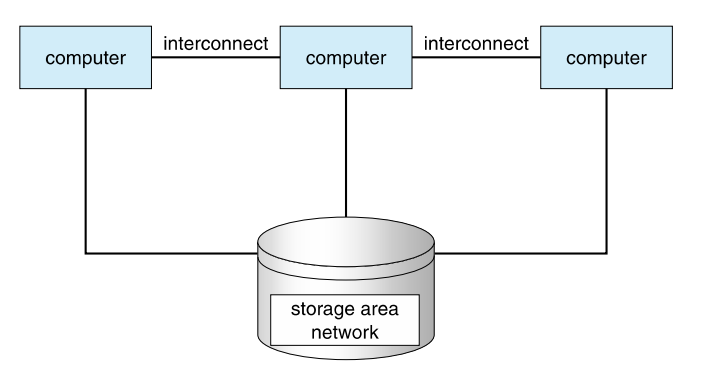
Distributed Systems
- Distribute the computation among several physical processors.
- Loosely coupled system – each processor has its own local memory; processors communicate with one another through various communications lines.
- Advantages of distributed systems.
- Resources Sharing
- Computation speed up – load sharing
- Reliability
- Communications
- Requires networking infrastructure.
- Local area networks (LAN) or Wide area networks (WAN)
- May be either client-server or peer-to-peer systems.
(생략)
- Network Operating System
- provides file sharing
- provides communication scheme
- runs independently from other computers on the network
- Distributed Operating System
- less autonomy between computers
- gives the impression there is a single operating system controlling the network.
Operating System Structure
- Multiprogramming (Batch system) needed for efficiency (non-preemptive multiprogramming)
- Single user cannot keep CPU and I/O devices busy at all times
- Multiprogramming organizes jobs (code and data) so CPU always has one to execute
- A subset of total jobs in system is kept in memory (job pool)
- One job selected and run via job scheduling
- job scheduling: 누가 먼저 스케쥴링 될 것인지
- When it has to wait (for I/O for example), OS switches to another job
- Timesharing (multitasking) is logical extension in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it is running, creating interactive computing
- Response time should be < 1 second
- good response time!
- Each user has at least one program executing in memory => process
- If several jobs ready to run at the same time => CPU scheduling
- If processes don’t fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run
- Virtual memory allows execution of processes not completely in memory
- Response time should be < 1 second
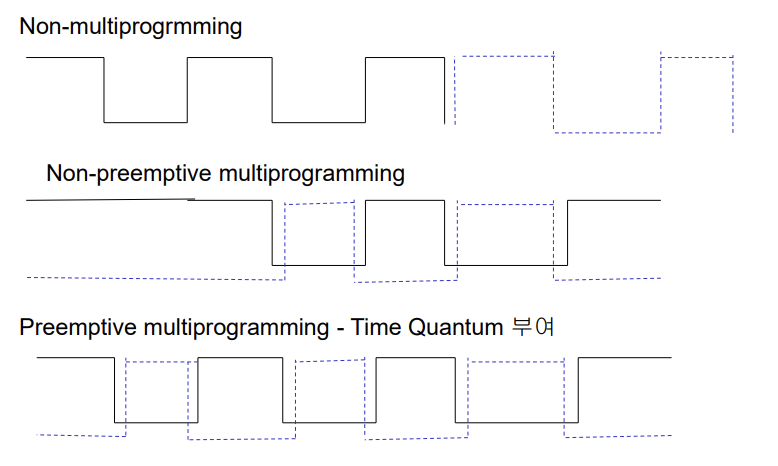
- Non-multiprogramming:
- 한 프로그램이 끝나고 다른 프로그램이 실행.
- CPU가 일을 하지 않고 놀고 있는 구간이 존재(CPU Time의 낭비)
- Non-preemptive multiprogramming
- CPU가 놀고 있는 구간을 활용하여 다른 프로그램을 실행시킴
- CPU가 쉬지 않고 일을 하여 시스템의 효율이 올라감
- CPU와 I/O device가 동시에 활용되는 경우가 생길 수 있음
- I/O를 하지 않는 동안에 CPU를 굉장히 오래 붙잡고 있어도 크게 문제가 되지 않는다.
- non preemptive - 강제로 빼앗지 않는
- I/O를 하기 위해서 자발적으로 내놓지 않으면 다른 프로그램이 실행될 수 없음
- pseudo parallel processing (실제로 둘이 같이 돌지 않기 때문에)
- Preemptive multiprogramming - Time Quantum 부여
- 어떤 프로그램이 CPU에서 실행이 되는데 CPU에서 실행될 수 있는 최대 시간이 바로 time quantum이다.
- time quantum 시간 동안만 CPU를 사용하는 것을 허락한다.
- I/O를 하지 않아도 CPU를 빼앗아서 동시에 다른 프로그램을 번갈아가면서 실행시킬 수 있음
- 만약 time quantum이 굉장히 커지게 되면 Non-preemptive 에 가까워 짐.
- 만약 time quantum이 굉장히 작아지게 되면 interaction은 굉장히 올라가는 대신에 시스템 성능은 오히려 Non-preemptive 보다 안 좋아 지게 된다.
- 그래서 적정한 값을 정하는 것이 중요함
Memory Layout for Multiprogrammed System

- 어떤 job(program)을 먼저 탑재시킬 지를 정하는 것이 job scheduling
- 탑재된 job들 중에서 누가 먼저 CPU를 차지할 지를 결정하는 것이 CPU scheduling
- swapping: 탑재된 job들 중에서 별로 시급하지 않은 job의 경우 hard disk job pool에 보내고(swap out) 더 중요한 job을 job pool(swap in)로부터 불러 들인다.
Operating-System Operations
- Interrupt driven (hardware and software)
- Hardware interrupt by one of the devices (외부 디바이스에 의한)
- Software interrupt (exception or trap):
- exception: Software error (e.g., division by zero)
- trap: Request for operating system service(시스템 콜을 호출하는 경우)
- Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system
- 정상적으로 실행되는 것처럼 보이지만 무한 루프를 돌고 있는 경우(interrupt 검출이 되지 않음)
- 이를 잡아낼 수 있는 tool이 있어야 함(아래와 같이)
- Basic tools to Ensure correct operation of computer system
- Dual mode - user가 kernel의 권한을 행사하지 못하도록 하는 것
- Privileged instruction
- Memory protection
- 프로그램이 OS 영역을 침범하거나 다른 프로그램을 침범하는 것을 catch하여 interrupt를 걸어 OS에 통보
- Timer interrupt – infinite loops
- 일정 시간이 경과하면 걸리는 interrupt
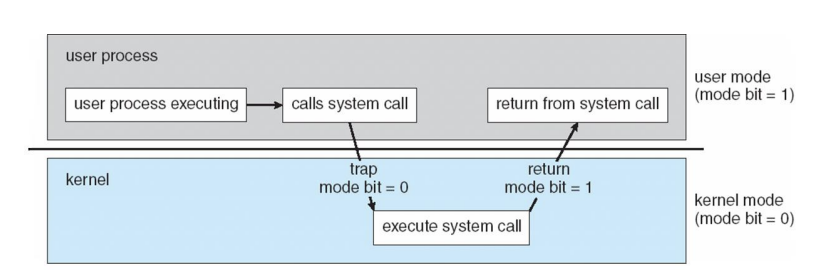
- Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and other system components
- User mode and kernel mode
- Mode bit provided by hardware (mode를 판단하기 위한 bit)
- Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code
- Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode
- 일부는 user mode에서 실행되지 않음(시스템에 심각한 문제를 야기하는 것을 방지하기 위함)
- System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user
- Increasingly CPUs support multi-mode operations
- i.e. virtual machine manager (VMM) mode for guest VMs
Transition from User to Kernel Mode
- Timer to prevent infinite loop / process hogging resources
- Timer is set to interrupt the computer after some time period
- Keep a counter that is decremented by the physical clock.
- Operating system set the counter (privileged instruction)
- When counter zero generate an interrupt -> 프로그램이 무한 루프를 돌고있다고 판단
- OS 자원을 낭비, CPU time 낭비
- Set up before scheduling process to regain control or terminate program that exceeds allotted time
- 종료 시켜 컴퓨터 자원 회수
Process Management(중요)
program definition은 어떤 프로그램의 모양(붕어빵틀) - 실행 파일
program definition이 만들어내는 instance가 process(msword 창을 두 개 띄우는 경우 '하나의 program definition에서 두 개의 process가 생겼다'라고 한다.; 틀로 찍어낸 붕어빵 두 개)
- A process is a program in execution. It is a unit of work within the system. Program is a passive entity, process is an active entity.
- 프로세스는 실제로 실행되고 있는 상태이기 때문에 active entity인 것.
- 변수 x도 선언 시에 메모리에 할당되는 것이 아니라 프로세스가 실행되면 할당 된다.
- Process needs resources to accomplish its task
- CPU, memory, I/O, files
- Initialization data
- Process termination requires reclaim of any reusable resources
Single-threaded processhas one program counter specifying location of next instruction to execute- 하나의 process에 하나의 program counter
- program counter가 갖는 값의 궤적이 바로 thread
- Process executes instructions sequentially, one at a time, until completion
Multi-threaded processhas one program counter per thread- Typically system has many processes, some user, some operating system running concurrently on one or more CPUs
- Concurrency by multiplexing the CPUs among the processes / threads
- CPU가 여러개인 경우 -> parallel processing
- CPU가 하나인 경우 -> pseudo parallel processing
- CPU 하나를 공유하면서 차지해야 하기 때문
Process Management Activities
The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with process management:
- Creating and deleting both user and system processes
- Suspending and resuming processes
- 프로세스가 계속 실행되는 것이 아니라 I/O를 해야 하기 때문에 I/O가 한 번 실행되고(suspend) 종료될 때(resume)까지 CPU에 의해 실행이 될 수 없다.
- Providing mechanisms for process synchronization
- 동일한 계좌에 대한 동기화
- Providing mechanisms for process communication (IPC- inter process ?)
- Providing mechanisms for deadlock handling
- 동기화를 하다가 잘못되면 두 프로세스 모두가 실행이 되지 않는 경우(둘 중 어느 프로세스도 이도저도 못하는 상황) 가 발생하는데
- 검출하여 해결하는 것이 process management의 역할
Memory Management
- To execute a program all (or part) of the instructions must be in memory
- All (or part) of the data that is needed by the program must be in memory.
- Memory management determines what is in memory and when
- Optimizing CPU utilization and computer response to users
- Memory management activities
- Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used and by whom
- Deciding which processes (or parts thereof) and data to move into and out of memory
- Allocating and deallocating memory space as needed
Storage Management
secondary memory
- OS provides uniform, logical view of information storage (3차원적 주소를 1차원으로 생각할 수 있도록 해 주는 역할)
- Abstracts physical properties to logical storage unit - file
- Each medium is controlled by device (i.e., disk drive, tape drive)
- Varying properties include access speed, capacity, data-transfer rate, access method (sequential or random)
- File-System management
- Files usually organized into directories
- Access control on most systems to determine who can access what
- OS activities include
- Creating and deleting files and directories
- Primitives to manipulate files and directories
- Mapping files onto secondary storage
- Backup files onto stable (non-volatile) storage media
Mass-Storage Management(생략)
- Usually disks used to store data that does not fit in main memory or data that must be kept for a “long” period of time
- Proper management is of central importance
- Entire speed of computer operation hinges on disk subsystem and its algorithms
- OS activities
- Free-space management
- Storage allocation
- Disk scheduling
- Some storage need not be fast
- Tertiary storage includes optical storage, magnetic tape
- Still must be managed – by OS or applications
- Varies between WORM (write-once, read-many-times) and RW (read-write)
Performance of Various Levels of Storage
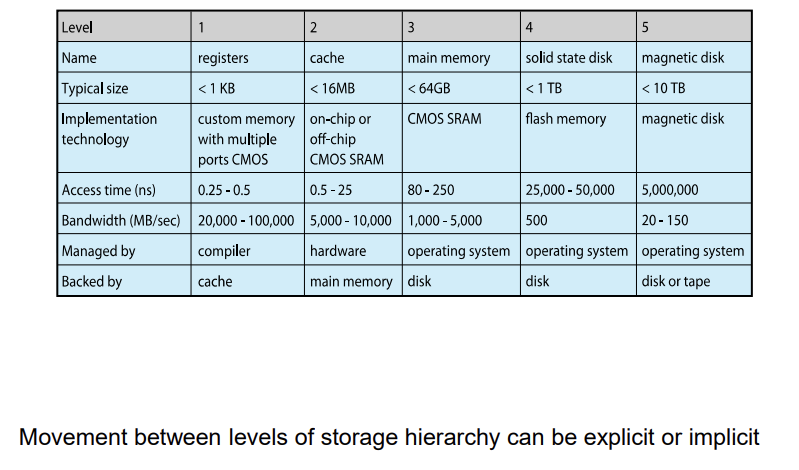
Migration of data "A" from Disk to Register
- Multitasking environments must be careful to use most recent value, no matter where it is stored in the storage hierarchy
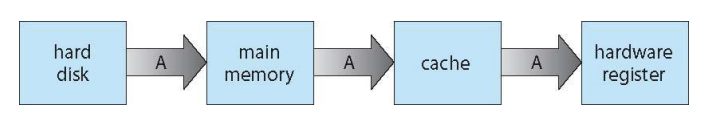
- Multiprocessor environment must provide cache coherency in hardware such that all CPUs have the most recent value in their cache
- multiprocessing 환경에서 더 어려운 과제 (하지만 중요한 OS의 필수 역할)
- Distributed environment situation even more complex
- Several copies of a datum can exist
- Various solutions covered in Chapter 17
I/O Subsystem
- One purpose of OS is to hide peculiarities of hardware devices from the user
- I/O subsystem responsible for
- Memory management of I/O including buffering (storing data temporarily while it is being transferred), caching (storing parts of data in faster storage for performance), spooling (the overlapping of output of one job with input of other jobs)
- General device-driver interface
- Drivers for specific hardware devices
Protection and Security
- Protection – any mechanism for controlling access of processes or users to resources defined by the OS
- Security – defense of the system against internal and external attacks
- Huge range, including denial-of-service, worms, viruses, identity theft, theft of service
- Systems generally first distinguish among users, to determine who can do what
- User identities (user IDs, security IDs) include name and associated number, one per user
- User ID then associated with all files, processes of that user to determine access control
- Group identifier (group ID) allows set of users to be defined and controls managed, then also associated with each process, file
- Privilege escalation(단계적 확대) allows user to change to effective ID with more rights
Computing Environments - Traditional Computing
- Stand-alone general purpose machines (network가 없던 시절)
- But blurred as most systems interconnect with others (i.e., the Internet)
- Office environment
- PCs connected to a network, terminals attached to mainframe or minicomputers providing batch and timesharing
- Now portals allowing networked and remote systems access to same resources
- Home networks
- Used to be single system, then modems
- Office environment
- Portals provide web access to internal systems
- Network computers (thin clients) are like Web terminals
- memory가 굉장히 적은 컴퓨터 (단순한)
- Mobile computers interconnect via wireless networks
- Networking becoming ubiquitous – even home systems use firewalls to protect home computers from Internet attacks
Computing Environments - Mobile Computing
- Handheld systems
- smartphones, tablets, etc
- What is the functional difference between them and a “traditional” laptop?
- Reduced feature set OS, limited I/O, limited CPU, memory, power
- Extra feature – more OS features (GPS, gyroscope)
- Allows new types of apps like augmented reality(AR)
- Use IEEE 802.11 wireless, or cellular data networks for connectivity
- Leaders are Apple iOS and Google Android
Computing Environments – Distributed Systems
- Distributed computiing
- Collection of separate, possibly heterogeneous, systems networked together
- Network is a communications path, TCP/IP most common
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Network is a communications path, TCP/IP most common
- Network Operating System provides features between systems across network
- Communication scheme allows systems to exchange messages
- Illusion of a single system
- Collection of separate, possibly heterogeneous, systems networked together
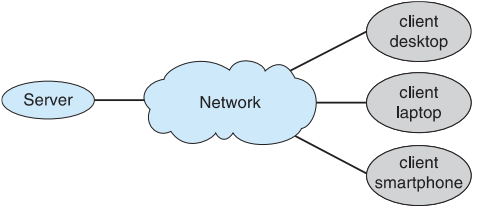
Computing Environments – Client-Server Computing
- Client-Server Computing
- Dumb terminals supplanted by smart PCs
- Many systems now servers, responding to requests generated by clients
- Compute-server system provides an interface to client to request services (i.e., database)
- File-server system provides interface for clients to store and retrieve files
Computing Environments - Peer-to-Peer Computing
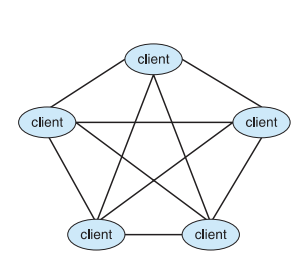
- Another model of distributed system
- P2P does not distinguish clients and servers
- Instead all nodes are considered peers
- May each act as client, server or both
- Node must join P2P network
- Registers its service with central lookup service on network, or
- Broadcast request for service and respond to requests for service via discovery protocol
- Examples include Napster and Gnutella, Voice over IP (VoIP) such as Skype
Computing Environments - Virtualization
- Allows operating systems to run applications as applications within other OS
- Vast and growing industry
- Emulation used when source CPU type different from target type (i.e. PowerPC to Intel x86)
- Generally slowest method
- When computer language not compiled to native code – Interpretation
- Every machine-level instruction that runs natively on source system must be translated to equivalent functions of target system
- Virtualization – OS natively compiled for CPU, running guest OSes also natively compiled
- Consider VMware running WinXP guests, each running applications, all on native WinXP host OS
- VMM (virtual machine Manager) provides virtualization services
- Use cases involve laptops and desktops running multiple OSes for exploration or compatibility
- Apple laptop running Mac OS X host, Windows as a guest
- Developing apps for multiple OSes without having multiple systems
- QA testing applications without having multiple systems
- Executing and managing compute environments within data centers
- VMM can run natively, in which case they are also the host
- There is no general purpose host then (VMware ESX and Citrix XenServer)
Virtual Machines
- A virtual machine takes the layered approach to its logical conclusion. It treats hardware and the operating system kernel as though they were all hardware.
- A virtual machine provides an interface identical to the underlying bare hardware.
- The operating system host creates the illusion that a process has its own processor and (virtual memory).
- Each guest provided with a (virtual) copy of underlying computer.
Computing Environments - Virtualization
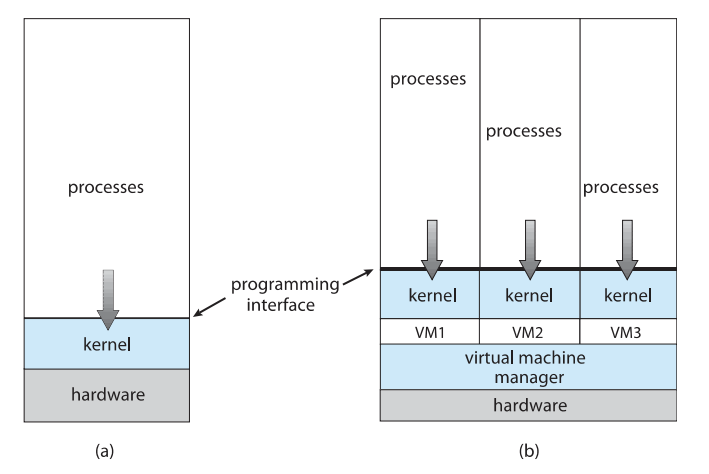
virtual machine manager
- 가상화를 해 주고 관리하는
여러 개의 실행환경이 생김
VMware Architecture
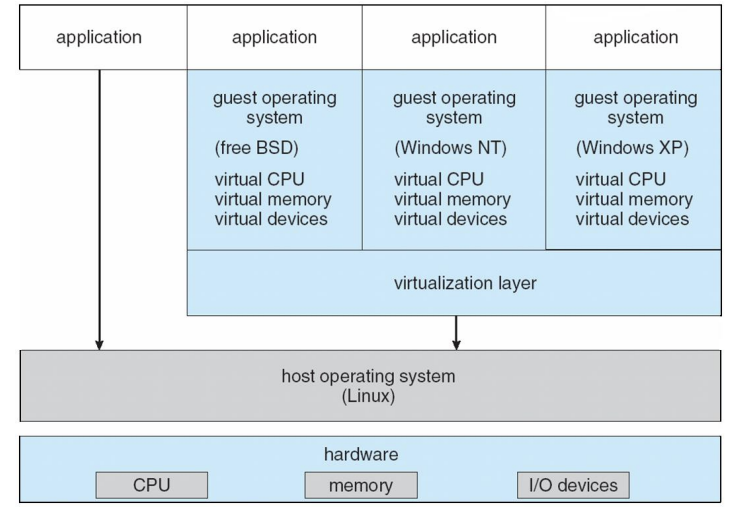
hardware위에 OS가 있고 그 위에 가상화 layer가 존재하는
application 별로 가상화 종류가 다 다름
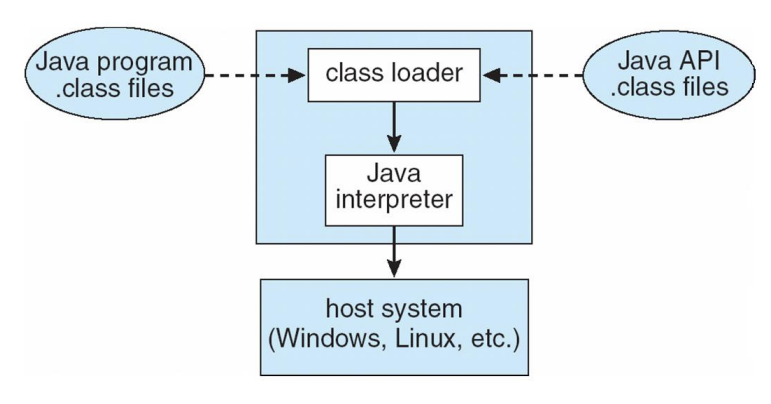
The Java Virtual Machine
Computing Environments – Cloud Computing
- Delivers computing, storage, even apps as a service across a network
- Logical extension of virtualization because it uses virtualization as the base for it functionality.
- Amazon EC2 has thousands of servers, millions of virtual machines, petabytes of storage available across the Internet, pay based on usage
- Many types
- Public cloud – available via Internet to anyone willing to pay
- Private cloud – run by a company for the company’s own use
- Hybrid cloud – includes both public and private cloud components
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – one or more applications available via the Internet (i.e., word processor)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – software stack ready for application use via the Internet (i.e., a database server)
- 플랫폼 자체를 서비스로 제공
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – servers or storage available over Internet (i.e., storage available for backup use)
- Infrastructure를 대여해 주는 서비스
- Cloud computing environments composed of traditional OSes, plus VMMs, plus cloud management tools
- Internet connectivity requires security like firewalls
- Load balancers spread traffic across multiple applications
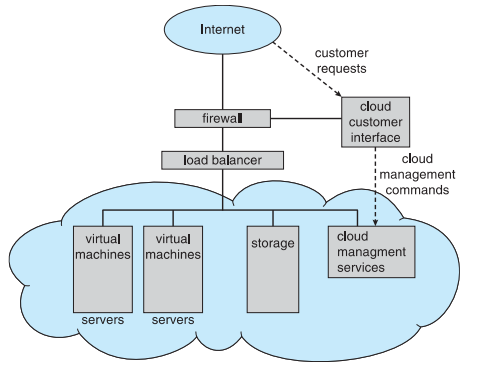
load balancer - 적절하게 load를 분배해야 최대 성능을 얻을 수 있음
Computing Environments – Real-Time Embedded Systems
- Real-time embedded systems most prevalent form of computers
- Car engine, manufacturing robots, Multimedia systems, network of diverse devices
- real-time OS
- Reduced feature set OS, limited user interface
- Various embedded systems (보통 임베디드 시스템에 있음, not 범용 컴퓨터)
- Some general-purpose computers with standard OS with special-purpose applications
- Some hardware devices with a special-purpose embedded OS
- some hardware devices with ASIC that perform tasks without an OS
- Real-time OS has well-defined fixed time constraints
- Processing must be done within constraint
- Correct operation only if constraints met
Real-Time Systems
- Often used as a control device in a dedicated application such as controlling scientific experiments, medical imaging systems, industrial control systems, and some display systems.
- 단순히 빠르기만 한 게 real-time os가 아님.
- Well-defined fixed-time constraints.
- time sharing systems : fast response
- Batch system: no time constraints
Hard real-time system- Secondary storage limited or absent, data stored in short-term memory, or read-only memory (ROM)
- Conflicts with time-sharing systems, not supported by general-purpose operating systems.
- 제한된 시간 안에 이벤트 처리가 100% 보장되는 시스템
Soft real-time system- Limited utility in industrial control or robotics
- Useful in applications (multimedia, virtual reality) requiring advanced operating-system features.
- ex. 전화 교환기
- 제한된 시간 안에 이벤트 처리가 100% 보장되지는 않지만 대부분 처리는 되는 시스템
Open-Source Operating Systems
- Operating systems made available in source-code format rather than just binary closed-source
- Linux, Windows
- Counter to the copy protection and Digital Rights Management (DRM) movement
- Started by Free Software Foundation (FSF), which has “copyleft” GNU Public License (GPL)
- Examples include GNU/Linux and BSD UNIX (including core of Mac OS X), and many more
- Can use VMM like VMware Player (Free on Windows), Virtualbox (open source and free on many platforms - http://www.virtualbox.com)
- Use to run guest operating systems for exploration
- I recommend to read textbook.
소중한 공감 감사합니다