[네트워크] 17. Connecting Devices and Virtual LANs
2023.02.13- -
17.1 Three Categories of Connecting Devices
- connecting 되는 범위에 따라서 세 가지 종류의 Device로 나뉜다.

- Hub
- At the physical layer: repeater or active hub
- Switch
- Link-layer switch
- Router
- network layer에서 connecting 시켜주는
Hubs or Repeaters
- A hub or a repeater operates only in the physical layers
- A hub or a repeater connects segments of a LAN
- A hub or a repeater forwards every frame; it has no filtering capability
- 걸러내는 기능이 없음, 받은 정보 모두를 나머지 link로 모두 forward시킨다.
- 전기적으로 오는 신호를 그냥 보내는 것이 hub
- To extend the LANs’ physical length
- hub로 온 내용을 모두에게 보내기 때문에 물리적인 거리가 extend 된다.
- 허브는 단순하게 모두에게 필터링 없이 다 보낸다.
- 그랬을 때 받았는데 자기 주소가 아닌 것이 판단되면 discard

Function of a Repeater

- 전송 매체를 통과했을 때 3 가지의 이유로 왜곡되는데 왜곡된 채로 신호를 amplifier하게 되면 왜곡이 더욱 커지기 때문에 regeneration을 위해 repeater를 거치게 된다.
- 이것이 repeater의 function
- regenerated signal
- 원래 전달되던 corrupted signal을 회복시키는 효과가 있다.
- 단순히 신호를 연장하는 기능을 하지만 그 연장하는 과정에서 들어온 신호를 amplifier, 즉 증폭만 시키는 것이 아니라 재생산해서 보냄으로써 connection이 확장된다 할 지라도 망가지는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
- 그러나 repeater 자체는 그런 신호 level에서의 regeneration은 가능하지만 이 자체가 외부로부터 들어온 신호를 filtering 한다던다 forwarding 하는 프로세스 방식이 다르다거나 하지는 않는다.
Repeaters/Hubs
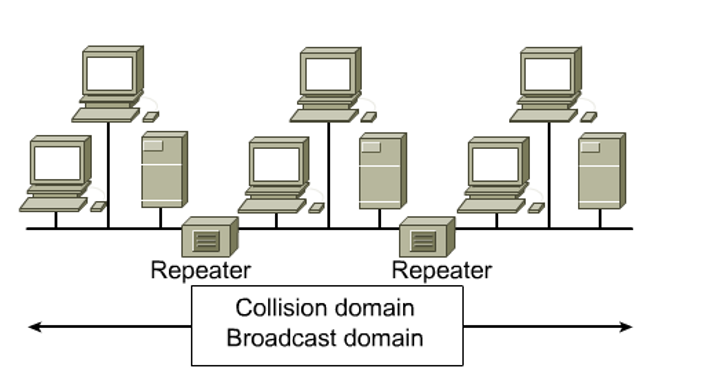
- 같은 collision domain 내에서 한 device가 데이터를 내 보내고 있는데 다른 device가 데이터를 내 보내면 collision이 발생한다.
- 그런데 repeater를 중간 중간에 두어 연결 하면 collision domain이 커지게 된다.(좋지 않음)
- 1,2,3,4층에 각각 LAN이 있는데 1층에 있는 LAN이 3층에 있는 LAN에 데이터를 보내는데 충돌이 발생하는 예시
- Repeaters are a Layer 1(physical layer) device that regenerates the signal, and passes it on
- Repeaters allow a longer end to end distance(extension)
- Repeaters increase the collision domain size
- Repeaters increase the broadcast domain size
- broadcast domain : 6바이트의 주소로 이루어져 있는 이더넷은 FFFFFF(all 1)의 경우 broadcast 방식으로 전달하게 되는데 이 경우의 전달 범위를 말한다.
(Link-Layer) Switches
hub, repeater보다는 더 지능적인 기능을 가진 device
physical layer 뿐만 아니라 data link layer까지 관여하기 때문에 frame의 MAC address를 읽어 원하는 device에만 보내는 것(filtering)이 가능하기 때문
- Filtering capability: Having a table used in filtering decisions
- switching table에 따른 filtering 여부 결정이 가능
- Does check, but does not change the physical (MAC) addresses in a frame
- frame의 MAC address를 확인은 하지만 변경하지 않는다.

- 어떤 디바이스로부터 1번 port로부터 데이터가 들어와서 destination 주소를 봤더니 해당 주소에 mapping 되는 port가 예를 들어 3번이었으면 3번 port로 다시 그것을 내보내는 역할을 한다.
- 나머지 port로는 내보내지 않도록 filtering
- hub, repeater처럼 쓸 데 없는 곳으로 보내지 않음으로써 트래픽 낭비가 일어나지 않게될 수 있다!
이후 관점: switch 안의 switching table이 어떤 방식으로 만들어지는가?
Switches
- Transparent switch(Learning switch이라고도 함; 학습을 해 가면서 테이블이 만들어지기 때문에)
- A switch in which the stations are completely unaware of the switch’s existence
- stations이 스위치의 존재를 완전히 모르는 스위치
- Three criteria for a transparent switch (IEEE 802.1d specification)
- Frames must forward from one station to another
- The forwarding table is automatically made by learning frame movements in the network
- Loops in the system must be prevented
- A switch in which the stations are completely unaware of the switch’s existence
Learning Switch

a. originally, 아무것도 없음(빈 상태)
b. After A sends a frame to D
- A -> D
- 처음에 스위치에는 어디로 갈 지 아무런 테이블의 내용이 존재하지 않기 때문에 A로부터 frame이 들어오면 하는 수 없이 스위치는 모두에게 forwarding 한다.
- 나머지 D가 아닌 station은 해당 정보를 discard하고 오로지 destination에 해당하는 D만 이를 수신함.
- 이 과정에서 1번 포트에는 A 기기가 있다는 사실을 알게 되어 이 사실이 기록됨.
c. After D sends a frame to B
d. After B sends a frame to A
e. After C sends a frame to D
- frame의 이동을 통해서 학습을 하게 되고 table이 만들어지고 table에 있는 내용을 토대로 forwarding 해야 할 포트가 점점 더 명확(transparent)해 진다.
- 이로써 더 효율적인 트래픽 사용이 가능.
- 무언가를 보내길 원해서 switch에 데이터를 보내는 디바이스는 자기의 정보가 털리는 느낌s
Loop Problem in a Learning Switch (a)
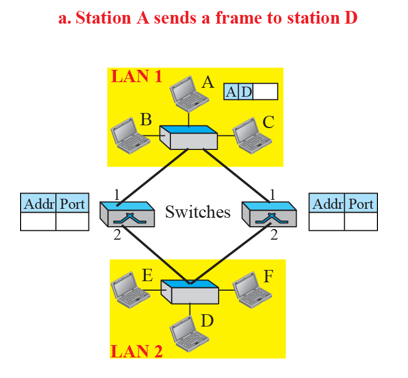
- A에서 D로 보내고 싶은 경우
- 중간에 한 개의 switch만 있다면 Loop가 발생하지 않지만 (안정성이나 이중화를 위해)어쩔 수 없이 Switch를 여러 개 두어야 하는 경우가 필연적으로 발생하기 때문에(For reliability) loop에 대한 처리를 어떻게 할 지 고려해 보아야 함.
Q) 하나의 LAN에서 여러 단말이 연결된 장치는 hub인 것인가? -> switch 임
Q) 왼쪽 switch에서 LAN2로 갔다가 오른쪽으로 가는 이유도 이해가 안되고 오른쪽 switch로 갔을 때 왜 그대로 A 주소를 가지고 있다가 A에 대한 내용으로 업데이트 되는 지도 이해가 가지 않는다.
A) 오른쪽으로 가는 이유는 주소를 아직 모르기 때문에 broadcast로 다 보내지는 것이고 원래의 정보(즉, packet 자체를)를 그대로 전달만 하는 것이기 때문에 A의 정보(도착지: D)가 담긴 packet이 전달되는 것
Loop Problem in a Learning Switch (b)

- 초기에는 transparent switch 테이블에 기록된 것이 없기 때문에 양 쪽 스위치 모두를 거쳐서 LAN2로 frame이 이동하게 되고 두 개의 copy frame이 생기게 된다.
- 이 과정에서 A주소를 가진 것이 1번 포트로 들어왔기 때문에 이를 양 쪽 스위치 모두 A의 주소를 학습하게 됨.
- 또한 각각 만들어진 frame 두 개가 다시 또 스위치로 보내지게 되는 문제가 발생한다.
Q) 이미 D가 수신을 한 것 같은데 왜 다시 스위치로 보내지는지??
A) 왼쪽 스위치에서 LAN2로 들어왔는데 이것이 다른 곳으로도 다 보내지기 때문에 다른 경로인 오른쪽 스위치로 다시 보내지기 때문, 근데 이 때 A가 2번으로 들어왔다고 생각될 것이기 때문에 table이 잘못 update 되는 것
Loop Problem in a Learning Switch (c)

- LAN1에서 LAN2로 가는 길 혹은 그 반대 길이 only one 이어야 하는데 여러 개가 있다보니 이러한 문제가 발생하게 되는 것이다.
- 다시 A라는 address를 가진 frame이 각 switch의 2번 port로 다시 전달되기 때문에 port의 번호가 바뀌어 A device가 2번 포트에 있는 걸로 잘못 기록되게 된다.
- 그래서 D가 수신했음에도 계속 해서 frame이 전달되는 문제가 발생
Loop Problem in a Learning Switch (d)

- 그래서 physical connection은 여러 개 이더라도 Logical connection은 하나가 되도록 한 길만 사용하다가 해당 길이 망가지게 되면 대체 길을 선택하여 그 길로 갈 수 있도록 하는 방식이 필요했고
- 이를 IEEE에서 표준화 한 것이 있다.
Connected LANs and its Graph

- LAN과 LAN을 연결하는 데 이중, 삼중의 switch가 존재하는 상황
- loop가 생기기 다분함.
- 쉽게 이해하기 위해 모든 cost 는 1로 정함.
- 두 개의 LAN을 거쳐서 가능 경우 cost 2
- outgoing(진입)만 cost가 존재
- switch에서 switch로 가는 여러 경로가 있겠지만 그 중에서 하나의 길만을 정해놓고 그 길로만 가도록 하는 방법을 알아볼 것이다.
Transparent Switches: Spanning Tree
- Spanning tree is a graph in which there is no loop
- To solve the looping problem, IEEE spec requires that switches use the spanning tree algorithm
- Select the root switch
- The one with the smallest built-in ID
- 가장 작은 시리얼 넘버를 갖는 것이 root switch로 설정
- The one with the smallest built-in ID
- Find the shortest path from the root switch to every other switch or LAN
- Combination of the shortest paths creates the shortest tree
- Mark the forwarding ports and blocking ports
Finding Shortest Paths and Spanning Tree

- 똑같은 cost의 두 가지 경로가 있다면 그 중 하나만 선택
- loop 문제를 해결
Spanning Tree: Forwarding and Blocking Ports

- S3에서 실질적으로 2번과 3번 port는 존재하지만 loop를 막기 위해 blocking 된다.
- 그런데 만약 S3의 1번 port에 문제가 생긴다면 새로 spanning tree를 만들어서 다른 경로로 들어올 수 있게 logical path를 만든다.
Broadcast and Collision Domains

- 각 Station 마다 bandwidth가 할당됨
- switch를 이용하게 되면 단말끼리 정보를 주고 받을 때 스위치가 갖는 필터링 기능 때문에 다른 domain으로 넘어가지 않는다.
- collision domain이 분리된다.
- 그러나 broadcasting의 경우에는 이를 필터링하지 않는다.
LAN Segmentation

- Isolated traffic between segments
- Achieve more bandwidth per user by creating smaller collision domains
- 한 domain에서의 충돌이 다른 domain에 영향을 주지 않는다.
- segment 사이의 독립된 traffic을 보장한다.
- 만약 허브를 썼다면 10Mbps의 collision domain 영역이 겹치게 되어 첫번째 구간에서 데이터를 내보내고 있으면 중간 구간에서는 데이터를 내보내지 못하게 됐을 것이다. (10Mbps를 전체가 공유하게 되는 비효율)
- 하나의 single collision domain일 것이기 때문
Router
- Three layer (physical, data-link, and network) device
- Major differences with repeater or switch
- To have a physical and logical (IP) address for each of its interfaces
- IP address를 보고 필터링 기능을 수행하는 것이 router의 목적
- To act only on those packets in which the link-layer destination address matches the address of the interface at which the packet arrives
- To change the link-layer address of the packet when it forwards the packet
- To have a physical and logical (IP) address for each of its interfaces
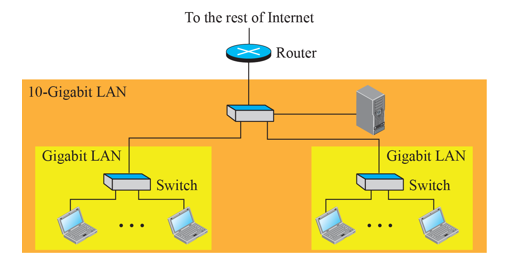
비마관 LAN(왼쪽 노란 박스), 참빛관 LAN(오른쪽 노란 박스) 가 있다고 하고 만약 고려대 친구에게 데이터를 전송하고자 한다면 router를 통해서 바깥 망으로 나가서 IP 주소를 찾은 후에 보낼 수 있게된다.
추후 network layer에 대해 배운 후 더 자세히 알아볼 것이다.
17.2 Virtual LANs
- LAN configured by software, not by physical wiring
- VLANs create broadcast domains

- software 적으로 switch를 조절하면 실제로(physically)는 비마관에 있는 device이지만 다른 참빛관에 있는 device, 옥의관에 있는 device 들과도 하나의 group(segment)처럼 묶인 것과 같이 생각될 수 있는 것이다.
- 이것이 Virtual LANs 의 개념.
- physical wiring에 구애받지 않고 새로운 가상의 segment를 형성할 수 있는 것
- Membership is characterized by interface numbers, MAC addresses, IP addresses, multicast IP addresses or a combination of the above
- Two switches in a backbone using VLAN software

- 동적으로 망을 운영하고 망의 segment를 만드는 것이 가능하기 때문에 많은 응용이 가능해 진다.
- Configuration
- VLAN can be configured in one of three ways: manual(관리자가 직접 설정), semiautomatic, and automatic
- Communication between switches
- Each switch must know not only which station belongs to which VLAN, but also the membership of stations connected to other switches
- Three methods are devised: table maintenance, frame tagging, and TDM(time division multiplexing)
- Advantages of VLAN
- Cost and time reduction
- Creating virtual workgroups
- Security
'CS 지식 > 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [네트워크] 19. Network-Layer Protocols (0) | 2023.02.13 |
|---|---|
| [네트워크] 18. Introduction to Network Layer (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 15. 무선 LAN(Wireless LANs) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 14. 다른 유선 네트워크(Other Wired networks) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
| [데이터 통신] 13. Wired LANs Ethernet(유선 LAN 이더넷) (0) | 2023.02.13 |
소중한 공감 감사합니다